Osteoporosis, often referred to as the “silent disease,” is a common skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, compromised bone strength, and an increased risk of fractures. This essay aims to provide a comprehensive overview of osteoporosis, including its definition, risk factors, causes, impact on individuals and society, diagnostic methods, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Understanding this condition is crucial for promoting bone health, reducing fracture risk, and improving quality of life for individuals affected by osteoporosis.
Defining Osteoporosis:
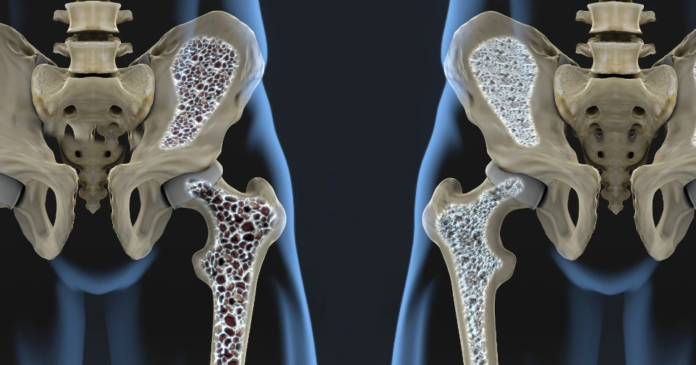
Osteoporosis is a progressive disease that weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. It occurs when the rate of bone resorption (breakdown) exceeds the rate of bone formation, resulting in a decrease in bone density and quality. As bone mass decreases, bones become porous, fragile, and prone to fractures, even with minor trauma.
Risk Factors and Causes:
Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Advancing age, female gender, menopause, a family history of the disease, and a personal history of fractures increase the risk. Other factors include low body weight, inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications (such as corticosteroids), and medical conditions that affect hormone levels or nutrient absorption.
Impact on Individuals and Society:
Osteoporosis has a significant impact on individuals’ physical, emotional, and social well-being. Fractures resulting from weakened bones can lead to pain, loss of mobility, decreased independence, and reduced quality of life. Fracture-related complications, such as prolonged hospitalization, increased healthcare costs, and the need for long-term care, impose a substantial burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
Diagnostic Methods:
The diagnosis of osteoporosis involves assessing bone mineral density (BMD) and evaluating fracture risk. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most commonly used method to measure BMD at the hip and spine. DXA results are reported as a T-score, comparing an individual’s BMD to the average BMD of young, healthy adults. Other diagnostic tools, such as quantitative ultrasound and CT scans, may provide additional information about bone health and fracture risk.
Prevention Strategies:
Preventing osteoporosis begins with building strong bones during childhood and adolescence. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercises, and a healthy lifestyle that includes avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are key preventive measures. Throughout adulthood, maintaining bone health through proper nutrition, exercise, and falls prevention strategies is crucial. Screening for risk factors and early intervention can help identify individuals who may benefit from preventive measures.
Treatment Options:
The management of osteoporosis focuses on reducing fracture risk and maintaining bone health. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, and balance exercises, help improve bone density, muscle strength, and balance. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake are essential for bone health and may be supplemented if dietary intake is insufficient. Medications, such as bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, denosumab, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), are prescribed to reduce bone loss, increase bone density, and decrease fracture risk.
Fall Prevention and Safety:
Preventing falls is crucial in reducing the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis. Measures such as removing hazards in the home, ensuring proper lighting, using assistive devices (such as handrails and grab bars), and regular vision check-ups contribute to fall prevention. Regular exercise to improve strength, balance, and coordination can also play a significant role in reducing falls and fractures.
Support and Education:
Providing support and education to individuals with osteoporosis is essential in promoting self-care and improving overall well-being. Support groups, counseling, and educational resources offer opportunities for individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and gain valuable information. Raising awareness about osteoporosis, its risk factors, and prevention strategies within the community is vital in fostering a culture of bone health and reducing the impact of this silent disease.
Osteoporosis is a common and debilitating condition that affects bone health and increases fracture risk. By understanding the definition, risk factors, causes, impact, diagnostic methods, prevention strategies, and treatment options, we can work towards promoting bone health, reducing fractures, and improving the quality of life for individuals living with osteoporosis. Through comprehensive approaches that combine lifestyle modifications, appropriate medical interventions, falls prevention strategies, and community support, we can mitigate the burden of osteoporosis on individuals, families, and society as a whole.